Energy dissipater is a structure provided behind an overflow section, for example a spillway, in order to dissipate the excess kinetic energy of water at downstream of the spillway. A spillway provided in the dam site always consists of an energy dissipating structure at the the toe of the dam. It kills the excess energy of surplus water and thus prevents damages to the dam and any other appurtenant structures in the downstream. Energy dissipation of water passing over the crest of spillway may be achieved by one of the following methods:
- Hydraulic Jump Type Stilling Basin
- Roller Bucket
- Deflector Bucket / Flip Bucket / Ski Jump Bucket / Trajectory Bucket
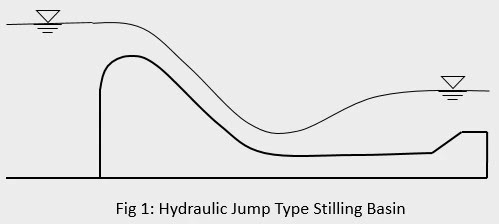
1. Hydraulic Jump Type Stilling Basin
An stilling basin is a structure provided at the toe of spillway in order to dissipate the energy of excess water coming from spillway by formation of hydraulic jump within the confines of the basin. The flow passing at critical depth over the crest of spillway becomes super critical at dam toe which when meets the normal flow at subcritical depth in the downstream side, a hydraulic jump is formed during the transition from super critical to subcritical flow. The stilling basin should be so designed that the hydraulic jump is formed within the length of the basin so as to not harm the channel behind the length of stilling basin. In order to achieve this, the post jump depth obtained from sequent depth relation should be exactly equal to tail water depth. A stilling basin consists of a concrete apron and some auxiliary structures such as end sill, chute blocks, baffle blocks, etc.
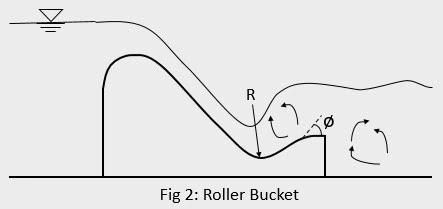
2. Roller Bucket
Roller bucket is used to dissipate the energy in situation when the tail water depth is much more than the post jump depth. When high velocity sheet of water slides down the spillway, it gets arrested by the tail water. As a result, excess energy is dissipated due to formation of submerged hydraulic jump. A roller may be either a solid roller bucket or a slotted roller bucket the latter being the improved version of the former. The bucket type energy dissipater has a relatively short length as compared to hydraulic jump type stilling basin. The major design parameters for a roller bucket are the radius of bucket (R) and lip angle $(\phi)$. The radius varies from 15 to 25 m and lip angle varies from 20° to 40°.
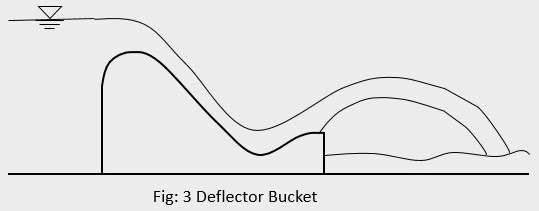
3. Deflector Bucket / Flip Bucket / Ski Jump Bucket / Trajectory Bucket
Deflector bucket is used to dissipate the energy in situation when the tail water depth is insufficient for the formation of hydraulic jump. i.e. tail water depth is much less than post jump depth. It is in construction very similar to roller bucket but the hydraulic action is entirely different. The trajectory bucket deflects the high velocity jet into the air and is made to strike the river bed at a considerable distance from the structure. This type of energy dissipater is suitable for the situation where foundation rock is of good quality and can withstand the erosive action of striking jet. The energy dissipation is achieved due to combined action of air resistance, viscous effect and turbulence due to impact on the river bed.